Sandstorm es una plataforma gratuita y de código abierto para servidores y aplicaciones web. Puede implementar muchas aplicaciones, incluidas WordPress, GitLab, MediaWiki, Apache Wave y el correo web de RoundCube con Sandstorm. Viene con una interfaz web simple y fácil de usar que lo ayuda a instalar y administrar aplicaciones en su servidor. En comparación con otras plataformas, Sandstorm está diseñado desde cero para ser radicalmente más fácil de usar.
En esta publicación, le mostraremos cómo instalar Sandstorm en CentOS 8 VPS.
Requisitos
- Un nuevo servidor CentOS 8 en Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform
- Una contraseña de root configurada en su servidor
Paso 1:crear el servidor en la nube de Atlantic.Net
Primero, inicie sesión en su servidor en la nube de Atlantic.Net. Cree un nuevo servidor, eligiendo CentOS 8 como sistema operativo con al menos 2 GB de RAM. Conéctese a su servidor en la nube a través de SSH e inicie sesión con las credenciales resaltadas en la parte superior de la página.
Una vez que haya iniciado sesión en su servidor CentOS 8, ejecute el siguiente comando para actualizar su sistema base con los últimos paquetes disponibles.
dnf update -y
Paso 2:configurar el nombre de host
Antes de comenzar, deberá establecer un nombre de host completo para su servidor. Puede configurarlo usando el siguiente comando:
hostnamectl set-hostname sandstorm.example.com
Una vez que haya terminado, puede continuar con el siguiente paso.
Paso 3:instalar Sandstorm
Sandstorm proporciona un script de instalación automática que facilita la instalación de Sandstorm en su servidor.
Puede descargar el script de instalación de Sandstorm usando el siguiente comando:
curl https://install.sandstorm.io >install.sh
Una vez descargado el script, ejecute el script descargado para iniciar la instalación:
bash install.sh
Se le pedirá que seleccione la opción de instalación como se muestra a continuación:
Sandstorm makes it easy to run web apps on your own server. You can have: 1. A typical install, to use Sandstorm (press enter to accept this default) 2. A development server, for working on Sandstorm itself or localhost-based app development
Presiona enter para seleccionar la opción predeterminada. Debería ver el siguiente resultado:
How are you going to use this Sandstorm install? [1] We're going to: * Install Sandstorm in /opt/sandstorm * Automatically keep Sandstorm up-to-date * Create a service user (sandstorm) that owns Sandstorm's files * Configure Sandstorm to start on system boot (with systemd) * Listen for inbound email on port 25. Rest assured that Sandstorm itself won't run as root. OK to continue? [yes]
Presiona enter continuar. Debería ver el siguiente resultado:
NOTE: It looks like your system already has some other web server installed
(port 80 and/or 443 are taken), so Sandstorm cannot act as your main
web server.
This script can set up Sandstorm to run on port 6080 instead,
without HTTPS. This makes sense if you're OK with typing the port number
into your browser whenever you access Sandstorm and you don't need
security. This also makes sense if you are going to set up a reverse proxy;
if so, see https://docs.sandstorm.io/en/latest/administering/reverse-proxy/
If you want, you can quit this script with Ctrl-C now, and go uninstall
your other web server, and then run this script again. It is also OK to
proceed if you want.
OK to skip automatic HTTPS setup & bind to port 6080 instead? [yes]
Presiona enter para vincular el puerto Sandstorm a 6080 . Debería ver el siguiente resultado:
Note: Sandstorm's storage will only be accessible to the group 'sandstorm'. As a Sandstorm user, you are invited to use a free Internet hostname as a subdomain of sandcats.io, a service operated by the Sandstorm development team. ... Sandcats.io protects your privacy and is subject to terms of use. By using it, you agree to the terms of service & privacy policy available here: https://sandcats.io/terms https://sandcats.io/privacy Choose your desired Sandcats subdomain (alphanumeric, max 20 characters). Type the word none to skip this step, or help for help. What *.sandcats.io subdomain would you like? [] none
Escriba ninguno y presione enter . Una vez que se haya completado la instalación, debería ver el siguiente resultado:
URL users will enter in browser: [http://sandstorm.example.com:6080] Sandstorm requires you to set up a wildcard DNS entry pointing at the server. This allows Sandstorm to allocate new hosts on-the-fly for sandboxing purposes. Please enter a DNS hostname containing a '*' which maps to your server. For example, if you have mapped *.foo.example.com to your server, you could enter "*.foo.example.com". You can also specify that hosts should have a special prefix, like "ss-*.foo.example.com". Note that if your server's main page is served over SSL, the wildcard address must support SSL as well, which implies that you must have a wildcard certificate. For local-machine servers, we have mapped *.local.sandstorm.io to 127.0.0.1 for your convenience, so you can use "*.local.sandstorm.io" here. If you are serving off a non-standard port, you must include it here as well. Wildcard host: [*.sandstorm.example.com:6080] Your server is now online! Visit this link to start using it: http://sandstorm.example.com:6080/setup/token/7f7f36c9e39f738a69564622123be64b373141a5 NOTE: This URL expires in 15 minutes. You can generate a new setup URL by running 'sudo sandstorm admin-token' from the command line. To learn how to control the server, run: sandstorm help
En este punto, Sandstorm está instalado y escuchando en el puerto 6080. Puede verificarlo con el siguiente comando:
ss -antpl | grep 6080
Debería ver la siguiente página:
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:6080 0.0.0.0:* users:(("sandstorm/gtway",pid=28336,fd=7),("sandstorm/montr",pid=28265,fd=7),("sandstorm/top",pid=28262,fd=7))
Paso 4:acceda a la interfaz de usuario web de Sandstorm
Ahora, abra su navegador web y acceda a Sandstorm usando la URL http://sandstorm.example.com:6080/setup/token/7f7f36c9e39f738a69564622123be64b373141a5 . Será redirigido a la siguiente página:
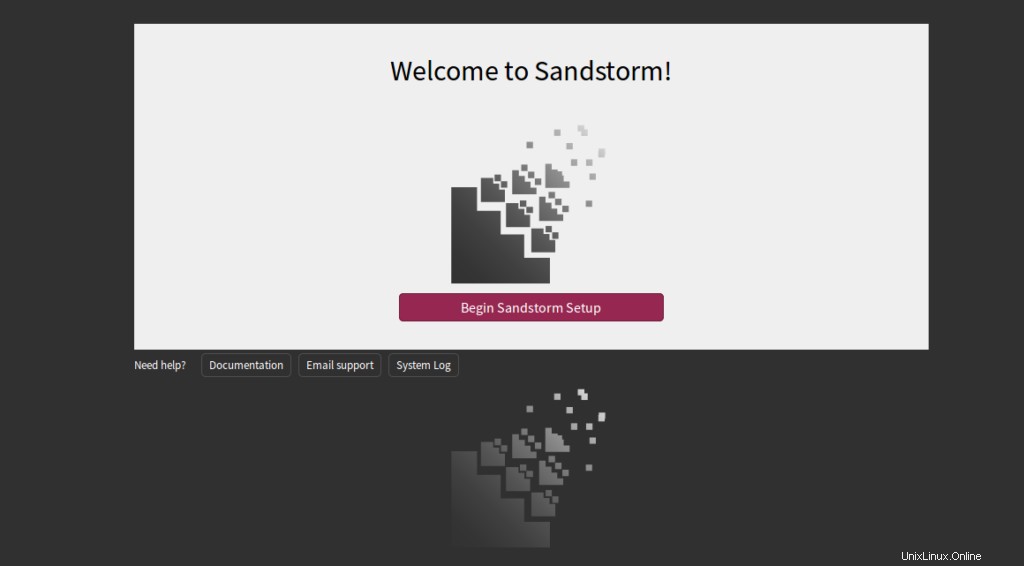
Haga clic en Comenzar configuración de Sandstorm . Debería ver la siguiente página:
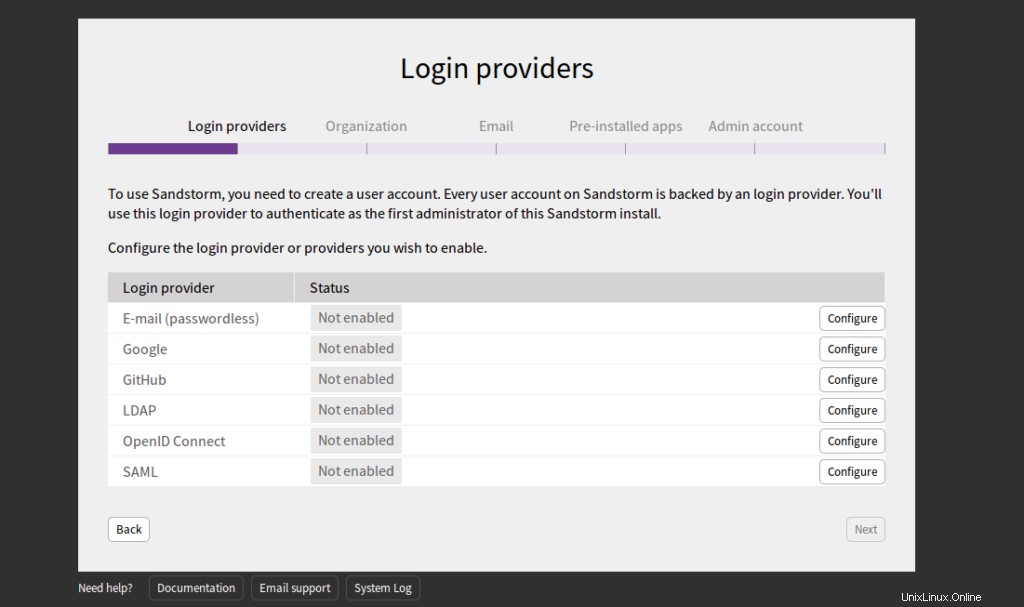
Seleccione Correo electrónico y haga clic en Configurar botón. Debería ver la siguiente página:
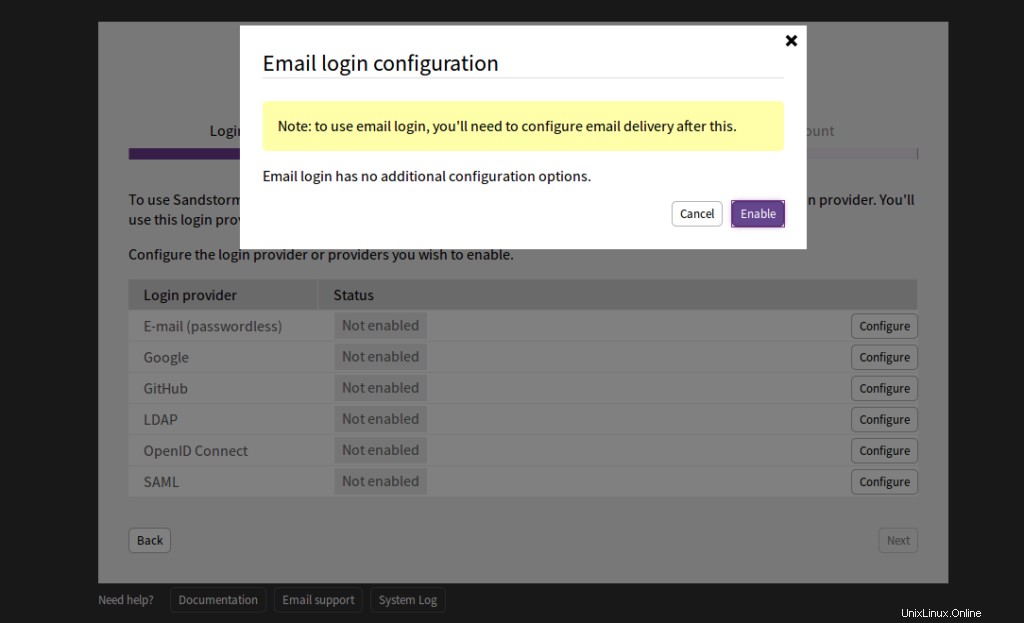
Haga clic en Habilitar . Debería ver la siguiente página:
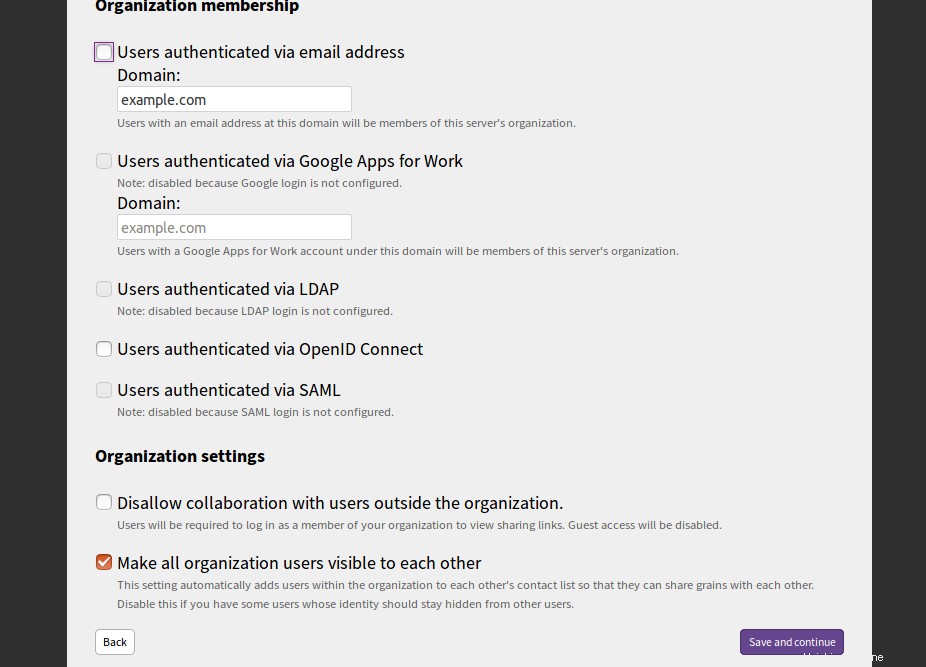
Proporcione el dominio de su servidor de correo y haga clic en Guardar y continuar botón. Debería ver la siguiente página:
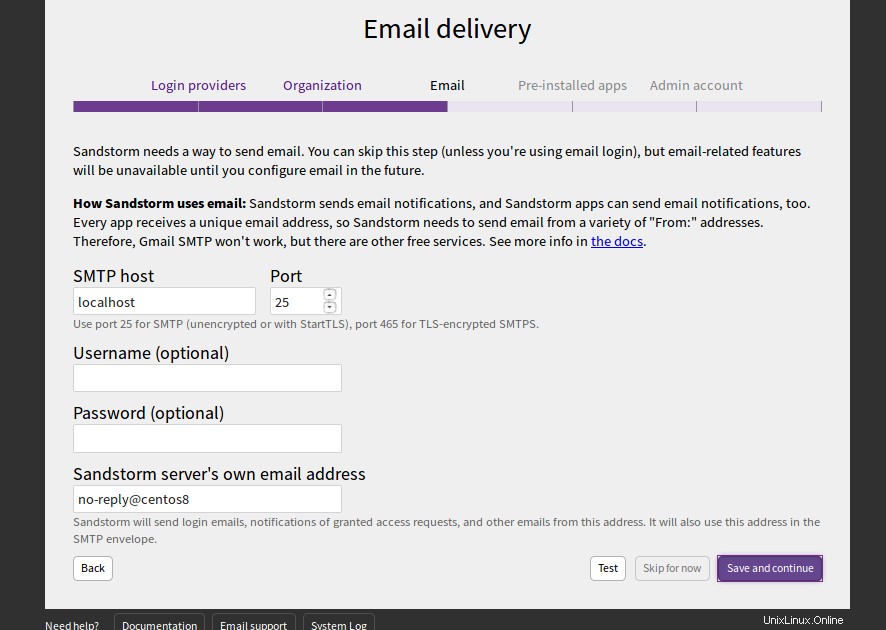
Proporcione su servidor SMTP, puerto, nombre de usuario y contraseña y haga clic en Guardar y continuar botón. Debería ver la siguiente página:
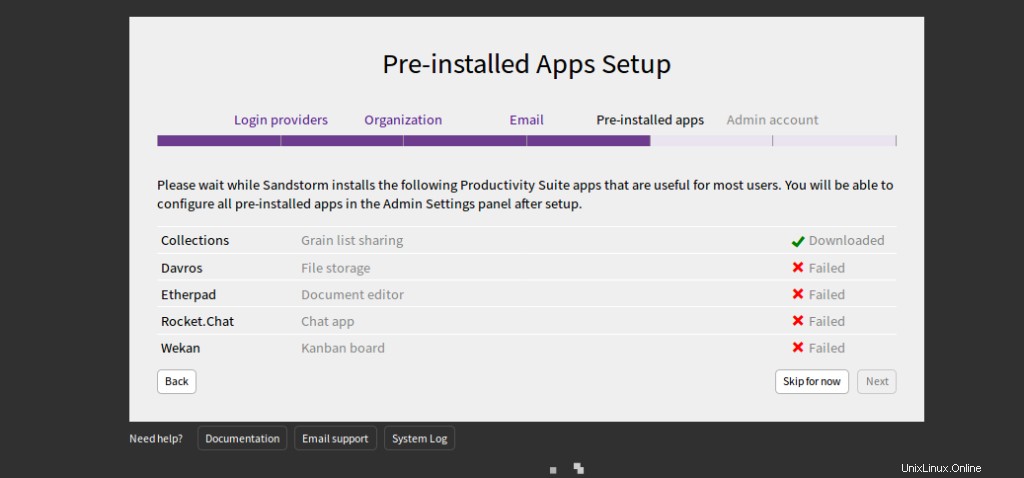
Haga clic en Omitir por ahora . Debería ver la siguiente página:
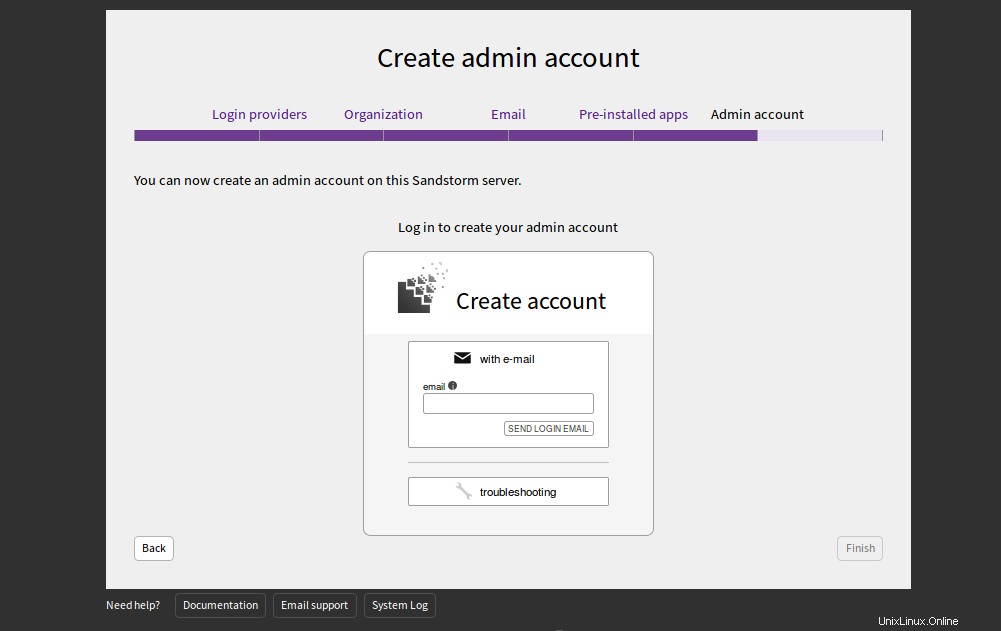
Proporcione su dirección de correo electrónico y haga clic en ENVIAR CORREO ELECTRÓNICO DE INICIO DE SESIÓN. Debería recibir un correo electrónico con las credenciales de inicio de sesión. Puede usar esas credenciales para iniciar sesión en el servidor de Sandstorm.
Conclusión
¡Felicidades! Ha instalado con éxito Sandstorm en CentOS 8 VPS. Sandstorm es una herramienta muy útil para los desarrolladores. Les ayuda a implementar cualquier aplicación con un solo clic. Para obtener más información y documentación sobre Sandstorm, visite su documentación.