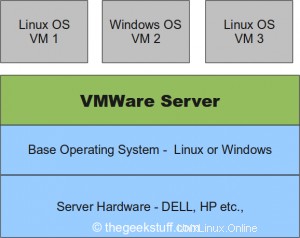
VMware Server se ejecuta sobre un sistema operativo host existente (Linux o Windows), como se muestra a continuación. Esta es una forma rápida de comenzar con VMware. Consulte nuestro artículo de introducción de VMware para obtener una comprensión de alto nivel sobre los fundamentos de la virtualización.
1. Descargar VMware Server 2
Vaya a la página de descarga de VMware Server. VMware Server 2 es gratuito. Sin embargo, debe registrarse en el sitio web de VMware para obtener la clave de licencia.
En la página de descarga están disponibles las siguientes opciones de descarga. En mi caso, descargué el formato binario .rpm.
- VMware Server 2 para sistemas operativos Windows:formato .exe binario
- VMware Server 2 para sistemas operativos Linux:formato binario .gz
- VMware Server 2 para sistemas operativos Linux:formato binario .rpm
2. Instale el servidor VMware 2
Instale VMware Server 2.0.2 rpm como se muestra a continuación.
# rpm -ivh VMware-server-2.0.2-203138.i386.rpm Preparing... ########################################### [100%] 1:VMware-server ########################################### [100%] The installation of VMware Server 2.0.2 for Linux completed successfully. You can decide to remove this software from your system at any time by invoking the following command: "rpm -e VMware-server". Before running VMware Server for the first time, you need to configure it for your running kernel by invoking the following command: "/usr/bin/vmware-config.pl". Enjoy, --the VMware team
3. Configure VMware Server 2 usando vmware-config.pl
Ejecute vmware-config.pl como se muestra a continuación. Asegúrese de ingresar el número de serie apropiado que obtuvo del sitio web de vmware.
Acepte los valores predeterminados para todo. La salida parcial de vmware-config.pl se muestra a continuación.
# /usr/bin/vmware-config.pl Do you accept? (yes/no) yes Do you want networking for your virtual machines? (yes/no/help) [yes] Please specify a name for this network. [Bridged] Your computer has multiple ethernet network interfaces available: eth0, eth1. Which one do you want to bridge to vmnet0? [eth0] Do you want to be able to use NAT networking in your virtual machines? (yes/no) [yes] Please specify a name for this network. [NAT] Do you want this program to probe for an unused private subnet? (yes/no/help) [yes] Do you wish to configure another NAT network? (yes/no) [no] Do you want to be able to use host-only networking in your virtual machines? [yes] Please specify a name for this network. [HostOnly] Do you want this program to probe for an unused private subnet? (yes/no/help [yes] Do you wish to configure another host-only network? (yes/no) [no] Please specify a port for remote connections to use [902] Please specify a port for standard http connections to use [8222] Please specify a port for secure http (https) connections to use [8333] The current administrative user for VMware Server is ''. Would you like to specify a different administrator? [no] Using root as the VMware Server administrator. In which directory do you want to keep your virtual machine files? [/var/lib/vmware/Virtual Machines] Please enter your 20-character serial number. Type XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX or 'Enter' to cancel: AAAAA-BBBBB-CCCCC-DDDDD Starting VMware services: Virtual machine monitor [ OK ] Virtual machine communication interface [ OK ] VM communication interface socket family: [ OK ] Virtual ethernet [ OK ] Bridged networking on /dev/vmnet0 [ OK ] Host-only networking on /dev/vmnet1 (background) [ OK ] DHCP server on /dev/vmnet1 [ OK ] Host-only networking on /dev/vmnet8 (background) [ OK ] DHCP server on /dev/vmnet8 [ OK ] NAT service on /dev/vmnet8 [ OK ] VMware Server Authentication Daemon (background) [ OK ] Shared Memory Available [ OK ] Starting VMware management services: VMware Server Host Agent (background) [ OK ] VMware Virtual Infrastructure Web Access Starting VMware autostart virtual machines: Virtual machines [ OK ] The configuration of VMware Server 2.0.2 build-203138 for Linux for this running kernel completed successfully.
4. Vaya a VMware Infrastructure Webaccess
Como parte de vmware-config.pl, inicia todos los servicios necesarios de VMware y también se agrega al script de inicio. Para verificar si todos los scripts de VMware se inician correctamente durante el inicio, reinicie el servidor.
Vaya a https://{host-os-ip}:8333/ui para acceder a la consola de acceso web de VMware Infrastructure. Esto le pedirá el nombre de usuario y la contraseña como se muestra a continuación. LoginName es raíz. La contraseña es la contraseña raíz del sistema operativo host.
 Figura: Inicio de sesión de acceso web de VMware
Figura: Inicio de sesión de acceso web de VMware
En el próximo artículo, discutiremos cómo crear una máquina virtual usando la infraestructura webaccess.