En el último tutorial, le mostré cómo configurar Samba en Centos 7 compilando Samba desde el código fuente, ya que el paquete proporcionado por RedHat no es compatible con Active Directory. Me di cuenta de que hay un repositorio llamado Wing que proporciona soporte AD a samba4 rpm. En este tutorial, usaré este repositorio para la instalación de Samba. También mostraré cómo crear un recurso compartido de samba.
En este tutorial, usaré un servidor CentOS 7 con una instalación mínima como base con SELinux habilitado.
Preparar el servidor CentOS 7
Compruebe el estado de SELinux.
[[email protected] ~]# sestatus SELinux status: enabled SELinuxfs mount: /sys/fs/selinux SELinux root directory: /etc/selinux Loaded policy name: targeted Current mode: enforcing Mode from config file: enforcing Policy MLS status: enabled Policy deny_unknown status: allowed Max kernel policy version: 28 [[email protected] ~]#
Haga una entrada en el archivo de host con la dirección IP del servidor seguida del nombre de host completo (fqdn) y luego la parte local del nombre de host.
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.1.190 samba4.sunil.cc samba4
[[email protected] ~]#
Instale el repositorio de Epel CentOS.
[[email protected] ~]# yum install epel-release -y
Instale los paquetes básicos.
[[email protected] ~]# yum install vim wget authconfig krb5-workstation -y
Ahora instala el repositorio del ala.
[[email protected] ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ [[email protected] yum.repos.d]# wget http://wing-net.ddo.jp/wing/7/EL7.wing.repo [[email protected] yum.repos.d]# sed -i '[email protected][email protected][email protected]' /etc/yum.repos.d/EL7.wing.repo [[email protected] yum.repos.d]# yum clean all Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Cleaning repos: base extras updates wing wing-source Cleaning up everything Cleaning up list of fastest mirrors [[email protected] yum.repos.d]#
Instalar Samba 4 en CentOS 7
Instalando los paquetes Samba4 desde el repositorio wing con yum.
[[email protected] yum.repos.d]# yum install -y samba45 samba45-winbind-clients samba45-winbind samba45-client\
samba45-dc samba45-pidl samba45-python samba45-winbind-krb5-locator perl-Parse-Yapp\
perl-Test-Base python2-crypto samba45-common-tools
Elimina estos archivos.
[[email protected] ~]# rm -rf /etc/krb5.conf
[[email protected] ~]# rm -rf /etc/samba/smb.conf
Configuración de Samba 4
Ahora haremos el aprovisionamiento del dominio.
[[email protected] ~]# samba-tool domain provision --use-rfc2307 --interactive
Realm [SUNIL.CC]:
Domain [SUNIL]:
Server Role (dc, member, standalone) [dc]:
DNS backend (SAMBA_INTERNAL, BIND9_FLATFILE, BIND9_DLZ, NONE) [SAMBA_INTERNAL]:
DNS forwarder IP address (write 'none' to disable forwarding) [4.2.2.1]:
Administrator password:
Retype password:
Looking up IPv4 addresses
Looking up IPv6 addresses
No IPv6 address will be assigned
Setting up secrets.ldb
Setting up the registry
Setting up the privileges database
Setting up idmap db
Setting up SAM db
Setting up sam.ldb partitions and settings
Setting up sam.ldb rootDSE
Pre-loading the Samba 4 and AD schema
Adding DomainDN: DC=sunil,DC=cc
Adding configuration container
Setting up sam.ldb schema
Setting up sam.ldb configuration data
Setting up display specifiers
Modifying display specifiers
Adding users container
Modifying users container
Adding computers container
Modifying computers container
Setting up sam.ldb data
Setting up well known security principals
Setting up sam.ldb users and groups
Setting up self join
Adding DNS accounts
Creating CN=MicrosoftDNS,CN=System,DC=sunil,DC=cc
Creating DomainDnsZones and ForestDnsZones partitions
Populating DomainDnsZones and ForestDnsZones partitions
Setting up sam.ldb rootDSE marking as synchronized
Fixing provision GUIDs
A Kerberos configuration suitable for Samba 4 has been generated at /var/lib/samba/private/krb5.conf
Setting up fake yp server settings
Once the above files are installed, your Samba4 server will be ready to use
Server Role: active directory domain controller
Hostname: samba4
NetBIOS Domain: SUNIL
DNS Domain: sunil.cc
DOMAIN SID: S-1-5-21-1578983437-3114190590-2362936743
[[email protected] etc]#
Asegúrese de que los puertos estén abiertos en el cortafuegos.
[[email protected] etc]#firewall-cmd --add-port=53/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=53/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=88/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=88/udp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=135/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=137-138/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=139/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=389/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=389/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=445/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=464/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=464/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=636/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=1024-3500/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=3268-3269/tcp --permanent [[email protected] ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
El paquete no proporciona el script de inicio, lo agregaremos ahora.
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/systemd/system/samba.service [Unit] Description= Samba 4 Active Directory After=syslog.target After=network.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/var/run/samba.pid ExecStart=/usr/sbin/samba [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target [[email protected] ~]# [[email protected] ~]# systemctl enable samba Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/samba.service to /etc/systemd/system/samba.service. [[email protected] ~]# systemctl restart samba
Todos los demás pasos son similares a mi artículo anterior
para configurar hosts de Windows y Linux, consúltelo
Instalación del controlador de dominio Samba4 desde la fuente
Creación del recurso compartido Samba con compatibilidad con Windows ACL
Necesitamos configurar ACL extendida para samba4. Agregue lo siguiente en el archivo smb.conf bajo global.
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
# Global parameters
[global]
------------
-------------
vfs objects = acl_xattr
map acl inherit = yes
store dos attributes = yes
------------
-------------
[[email protected] ~]#
Ahora reinicie el servicio Samba.
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl restart samba
Solo los usuarios y grupos que tengan el privilegio SeDiskOperatorPrivilege otorgado pueden configurar permisos para compartir.
[[email protected] ~]# net rpc rights grant "SUNIL\Domain Admins" SeDiskOperatorPrivilege -U "USER\administrator" Enter USER\administrator's password: Successfully granted rights. [[email protected] ~]#
Antes de crear el recurso compartido, debemos asegurarnos de que el servidor samba4 se autentique consigo mismo.
No podemos usar el método habitual ya que no funciona porque el paquete existente de wing entrará en conflicto con los paquetes proporcionados por RedHat, no podemos usar sssd aquí. Usaremos winbind para que esto funcione.
Utilice el siguiente método. Esto es necesario para crear el recurso compartido de samba con permisos específicos
Instale el siguiente paquete.
[[email protected] ~]#yum -y install authconfig-gtk*
Ejecute el comando.
[[email protected] yum.repos.d]# authconfig-tui
seleccione winbind, siga los siguientes pasos.
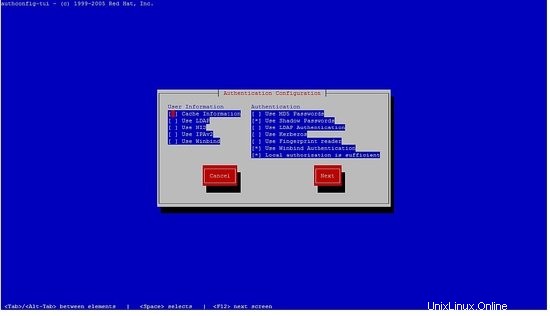
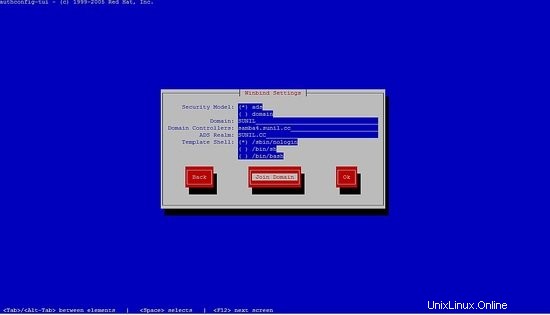
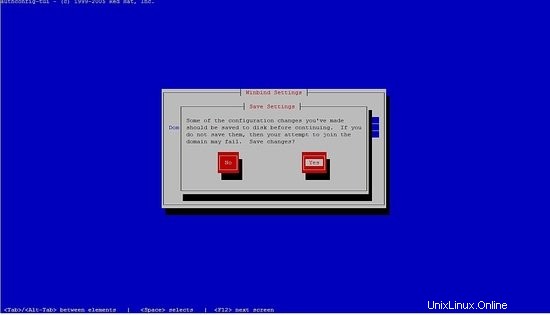
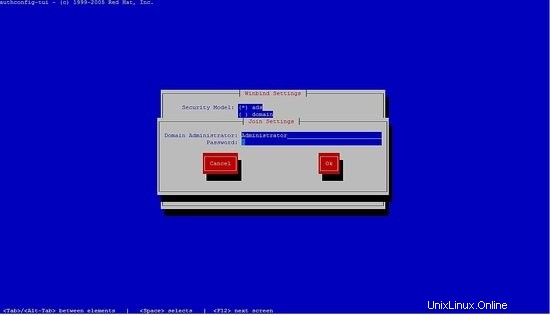
No podrá ingresar la contraseña, solo presione ok.
Luego comente las líneas en /etc/samba/smb.conf y reinicie el servicio samba.
Su configuración debería verse así:
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
# Global parameters
[global]
#--authconfig--start-line--
# Generated by authconfig on 2017/05/26 17:23:04
# DO NOT EDIT THIS SECTION (delimited by --start-line--/--end-line--)
# Any modification may be deleted or altered by authconfig in future
# workgroup = SUNIL
# password server = samba4.sunil.cc
# realm = SUNIL.CC
# security = ads
# idmap config * : range = 16777216-33554431
# template shell = /sbin/nologin
# kerberos method = secrets only
# winbind use default domain = false
# winbind offline logon = false
#--authconfig--end-line--
netbios name = SAMBA4
realm = SUNIL.CC
workgroup = SUNIL
dns forwarder = 4.2.2.1
server role = active directory domain controller
idmap_ldb:use rfc2307 = yes
vfs objects = acl_xattr
map acl inherit = yes
store dos attributes = yes
[netlogon]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol/sunil.cc/scripts
read only = No
[sysvol]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol
read only = No
[[email protected] ~]#
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl restart samba
Compruebe si podemos completar los usuarios y grupos:
[[email protected] ~]# wbinfo -u SUNIL\administrator SUNIL\sambauser SUNIL\testuser SUNIL\krbtgt SUNIL\guest [[email protected] ~]# wbinfo -g SUNIL\cert publishers SUNIL\ras and ias servers SUNIL\allowed rodc password replication group SUNIL\denied rodc password replication group SUNIL\dnsadmins SUNIL\enterprise read-only domain controllers SUNIL\domain admins SUNIL\domain users SUNIL\domain guests SUNIL\domain computers SUNIL\domain controllers SUNIL\schema admins SUNIL\enterprise admins SUNIL\group policy creator owners SUNIL\read-only domain controllers SUNIL\dnsupdateproxy [[email protected] ~]#
Modifique las líneas en nsswitch.conf:
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/nsswitch.conf ---------- --------- passwd: files winbind shadow: files winbind group: files winbind hosts: files dns wins services: files winbind netgroup: files winbind --------- ----------
Ahora verifique si podemos obtener el nombre de usuario usando el comando id:
[[email protected] ~]# id testuser uid=3000019(SUNIL\testuser) gid=100(users) groups=100(users),3000019(SUNIL\testuser),3000009(BUILTIN\users) [[email protected] ~]#
Crear un recurso compartido de Samba
Crearé dos recursos compartidos, uno solo accesible para testuser y el otro recurso compartido accesible para todos los usuarios en el grupo de usuarios del dominio.
El recurso compartido accesible por testuser se llamará testshare.
El recurso compartido accesible por todos los usuarios se denominará commonshare.
[[email protected] ~]# mkdir /testshare [[email protected] ~]# mkdir /commonshare [[email protected] ~]# chmod 770 /testshare [[email protected] ~]# chmod 770 /commonshare [[email protected] ~]# chown -R root:testuser /testshare [[email protected] ~]# chown -R root:"Domain Users" /commonshare
Ahora agregue las entradas en smb.conf
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
# Global parameters
[global]
netbios name = SAMBA4
realm = SUNIL.CC
workgroup = SUNIL
dns forwarder = 4.2.2.1
server role = active directory domain controller
idmap_ldb:use rfc2307 = yes
vfs objects = acl_xattr
map acl inherit = yes
store dos attributes = yes
[netlogon]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol/sunil.cc/scripts
read only = No
[sysvol]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol
read only = No
[TestShare]
comment = Test share accessible by testuser
path = /testshare
valid users = SUNIL\testuser
writable = yes
read only = no
force create mode = 0660
create mask = 0770
directory mask = 0770
force directory mode = 0770
access based share enum = yes
hide unreadable = yes
[CommonShare]
comment = Accessible by all the users
path = /commonshare
valid users = "@SUNIL\Domain Users"
writable = yes
read only = no
force create mode = 0660
create mask = 0777
directory mask = 0777
force directory mode = 0770
access based share enum = yes
hide unreadable = yes
[[email protected] ~]#
Reinicie el servicio samba.
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl restart samba
Acceda al recurso compartido de samba como usuario de prueba.
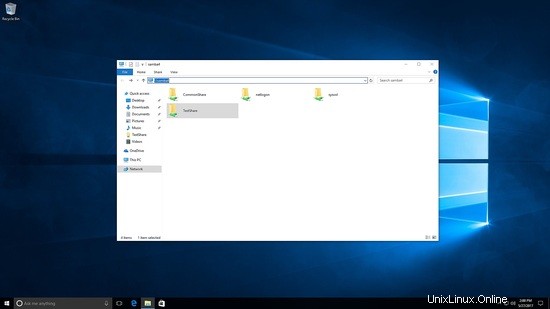
Aquí verá que tanto testshare como commonshare están visibles.
Probado creando archivos y carpetas bajo testshare.
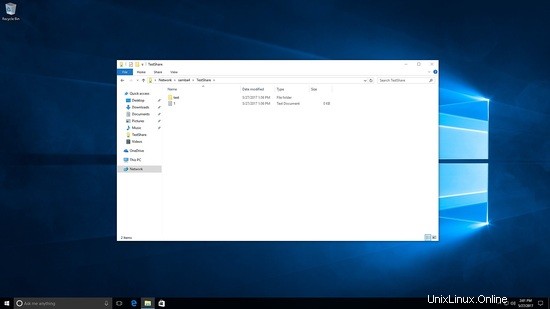
[[email protected] /]# cd /testshare/ [[email protected] testshare]# ls -l total 8 -rwxrwx---+ 1 SUNIL\testuser users 0 May 27 22:56 1.txt drwxrwx---+ 2 SUNIL\testuser users 6 May 27 22:56 test [[email protected] testshare]#
Ahora estoy iniciando sesión como un usuario diferente, solo se ve commonshare:
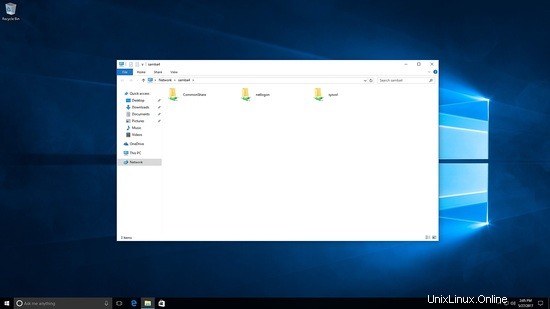
Creando archivos bajo commonshare.
[[email protected] commonshare]# ls -l total 8 drwxrwxrwx+ 2 SUNIL\testuser users 6 May 27 23:02 test drwxrwxrwx+ 2 SUNIL\sambauser users 6 May 27 23:07 test2 [[email protected] commonshare]#
Así es como creamos recursos compartidos en Samba 4.