Lo mejor que encontré fue usar el indicador -O (tenga en cuenta que no funciona en todas las distribuciones, usando Linux Mint 17.1 Rebecca IPUTILS-PING 3:20121221-4ubuntu1.1)
$ ping -O 10.10.5.1
64 bytes from 10.10.5.1: icmp_seq=53 ttl=245 time=460 ms
no answer yet for icmp_seq=54
64 bytes from 10.10.5.1: icmp_seq=55 ttl=245 time=265 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.5.1: icmp_seq=56 ttl=245 time=480 ms
no answer yet for icmp_seq=57
64 bytes from 10.10.5.1: icmp_seq=58 ttl=245 time=348 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.5.1: icmp_seq=59 ttl=245 time=515 ms
no answer yet for icmp_seq=60
64 bytes from 10.10.5.1: icmp_seq=61 ttl=245 time=320 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.5.1: icmp_seq=62 ttl=245 time=537 ms
Desde la página del manual:
-O Report outstanding ICMP ECHO reply before sending next packet.
This is useful together with the timestamp -D to log output to a
diagnostic file and search for missing answers.
fping no funcionó para mí... En mi caso, la mayoría de las veces quiero ver que esto es básicamente durante el reinicio del servidor... funciona bastante bien en Windows...
Construí un script simple (expandiendo la respuesta de @entropo) para ayudarme en eso, lo que puede ayudar a responder esta pregunta:
https://gist.github.com/brunobraga/7259197
#!/bin/bash
host=$1
if [ -z $host ]; then
echo "Usage: `basename $0` [HOST]"
exit 1
fi
while :; do
result=`ping -W 1 -c 1 $host | grep 'bytes from '`
if [ $? -gt 0 ]; then
echo -e "`date +'%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S'` - host $host is \033[0;31mdown\033[0m"
else
echo -e "`date +'%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S'` - host $host is \033[0;32mok\033[0m -`echo $result | cut -d ':' -f 2`"
sleep 1 # avoid ping rain
fi
done
Y el uso es algo como:
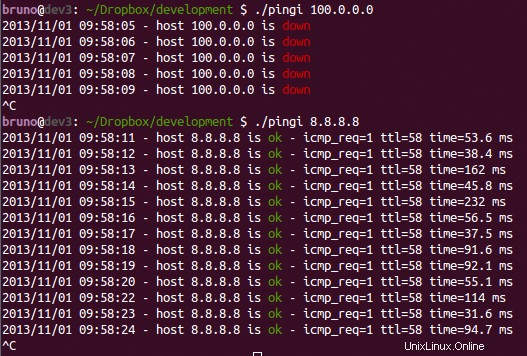
Cuando uso ping para ver si un host está activo en scripts de shell, hago algo como esto:
ping -W 1 -c 1 $HOST 2>&1 > /dev/null || (echo -n "dead!"; false) && command-that-needs-host-to-be-up
Básicamente, envía un ICMP que se agota en un segundo sin salida y usa el código de salida para activar más acciones.