Lighttpd es un servidor web gratuito, de código abierto y de alta velocidad especialmente diseñado para entornos de velocidad crítica. Requiere un bajo consumo de memoria en comparación con otros servidores web, como Apache y Nginx, y es especialmente rápido para ejecutar aplicaciones AJAX. Lighttpd también nos permite alojar aplicaciones web escritas en otro lenguaje de programación utilizando las interfaces FastCGI, SCGI y CGI. Lighttpd es la mejor opción para usted si su servidor sufre problemas de carga.
En este tutorial, aprenderemos cómo instalar Lighttpd en Debian 10 con soporte para PHP-FPM y MariaDB y protegeremos el servidor web con un certificado Let's Encrypt SSL.
Requisitos
- Un servidor que ejecuta Debian 10.
- Se ha configurado una contraseña de root para su servidor.
Usaré el nombre de dominio ejemplo.com en este tutorial. Reemplace example.com en todos los nombres de archivo y ajustes de configuración con su propio nombre de dominio a continuación.
Cómo empezar
Antes de comenzar, deberá actualizar su sistema con la última versión. Puede hacerlo ejecutando el siguiente comando:
apt-get update -y
apt-get upgrade -y
Una vez que su servidor esté actualizado, reinícielo para aplicar los cambios.
Instalar Lighttpd
De forma predeterminada, Lighttpd está disponible en el repositorio predeterminado de Debian 10. Puede instalarlo simplemente ejecutando el siguiente comando:
apt-get install lighttpd -y
Una vez finalizada la instalación, inicie el servicio Lighttpd y habilítelo para que se inicie después de reiniciar el sistema con el siguiente comando:
systemctl start lighttpd
systemctl enable lighttpd
También puede verificar el estado de Lighttpd con el siguiente comando:
systemctl status lighttpd
Deberías obtener el siguiente resultado:
? lighttpd.service - Lighttpd Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/lighttpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2019-09-06 02:09:35 EDT; 29s ago
Main PID: 4445 (lighttpd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 1138)
Memory: 1.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/lighttpd.service
??4445 /usr/sbin/lighttpd -D -f /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf
Sep 06 02:09:35 debian systemd[1]: Starting Lighttpd Daemon...
Sep 06 02:09:35 debian systemd[1]: Started Lighttpd Daemon.
Sep 06 02:09:36 debian systemd[1]: /lib/systemd/system/lighttpd.service:6: PIDFile= references path below legacy directory /var/run/, updating
lines 1-12/12 (END)
Una vez que haya terminado, puede continuar con el siguiente paso.
Instalar servidor MariaDB
Puede instalar el servidor MariaDB ejecutando el siguiente comando:
apt-get install mariadb-server mariadb-client -y
Una vez instalado, deberá asegurar la instalación de MariaDB. Puede asegurarlo ejecutando el siguiente script:
mysql_secure_installation
Answer all the questions as shown below: Change the root password? [Y/n] n Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
Una vez que haya terminado, puede continuar con el siguiente paso.
Instalar PHP y PHP-FPM
A continuación, deberá instalar PHP, PHP-FPM y FastCGI en su sistema. De forma predeterminada, Debian 10 se envía con la versión 7.3 de PHP. Puede instalarlo simplemente ejecutando el siguiente comando:
apt-get install php php-cgi php-fpm php-mysql -y
Una vez que todos los paquetes estén instalados, deberá editar el archivo php.ini y establecer cgi.fix_pathinfo en 1. Puede hacerlo con el siguiente comando:
nano /etc/php/7.3/fpm/php.ini
Cambie la siguiente línea:
cgi.fix_pathinfo=1
Guarde y cierre el archivo cuando haya terminado.
Por defecto, PHP apunta al socket UNIX /var/run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock. Por lo tanto, deberá configurar el grupo PHP-FPM para configurar las escuchas de PHP en el socket TCP.
Puede hacerlo editando el archivo /etc/php/7.3/fpm/pool.d/www.conf:
nano /etc/php/7.3/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
Busque la siguiente línea:
listen = /run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock
Y reemplácelo con la siguiente línea:
listen = 127.0.0.1:9000
Guarde y cierre el archivo cuando haya terminado. Luego, reinicie el servicio PHP-FPM para aplicar los cambios de configuración:
systemctl restart php7.3-fpm
A continuación, deberá modificar el archivo 15-fastcgi-php.conf:
nano /etc/lighttpd/conf-available/15-fastcgi-php.conf
Encuentra las siguientes líneas:
"bin-path" => "/usr/bin/php-cgi", "socket" => "/var/run/lighttpd/php.socket",
Y reemplácelos con los siguientes:
"host" => "127.0.0.1", "port" => "9000",
Guarde y cierre el archivo cuando haya terminado. Luego, habilite los módulos FastCGI y FastCHI-PHP con los siguientes comandos:
lighty-enable-mod fastcgi
lighty-enable-mod fastcgi-php
Finalmente, reinicie el servicio Lighttpd para aplicar los cambios:
systemctl restart lighttpd
Crear host virtual Lighttpd
A continuación, deberá crear un nuevo archivo de host virtual para probar PHP con Lighttpd. Puedes crearlo con el siguiente comando:
nano /etc/lighttpd/conf-available/example.com.conf
Agregue las siguientes líneas:
$HTTP["host"] == "www.example.com" {
server.document-root = "/var/www/html/"
server.errorlog = "/var/log/lighttpd/example.com-error.log"
}
Guarde y cierre el archivo cuando haya terminado. Luego, habilite el host virtual con el siguiente comando:
ln -s /etc/lighttpd/conf-available/example.com.conf /etc/lighttpd/conf-enabled/
A continuación, cree un archivo index.php de muestra en el directorio raíz del documento Lighttpd con el siguiente comando:
nano /var/www/html/index.php
Agregue la siguiente línea:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Guarde y cierre el archivo. Luego, cambie la propiedad del directorio raíz del documento Lighttpd a www-data con el siguiente comando:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/
Finalmente, reinicie el servicio Lighttpd para aplicar todos los cambios de configuración:
systemctl restart lighttpd
Asegure Lighttpd con Let's Encrypt Free SSL
Primero, deberá instalar la herramienta Certbot para proteger su servidor web con Let's Encrypt. De forma predeterminada, la última versión de Certbot no está disponible en el repositorio predeterminado de Debian 10.
Puede agregar el repositorio de Certbot con el siguiente comando:
apt-get install software-properties-common
add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
A continuación, actualice el repositorio e instale Certbot con el siguiente comando:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install certbot -y
A continuación, cree un certificado de Let's Encrypt con el siguiente comando:
certbot certonly --webroot -w /var/www/html/ -d www.example.com
Se le pedirá que proporcione su dirección de correo electrónico y acepte el término de la licencia como se muestra a continuación:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator webroot, Installer None Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y
Una vez que los certificados se hayan descargado correctamente, debería ver el siguiente resultado:
IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2019-12-06. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
A continuación, deberá combinar el certificado y la clave privada en un solo archivo. Puedes hacerlo con el siguiente comando:
cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/cert.pem /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem > /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/web.pem
A continuación, deberá editar el archivo de host virtual Lighttpd y definir la ruta del certificado Let's Encrypt SSL.
Puedes hacerlo con el siguiente comando:
nano /etc/lighttpd/conf-enabled/example.com.conf
Cambie el archivo como se muestra a continuación:
$HTTP["host"] == "www.example.com" {
server.document-root = "/var/www/html/"
}
$SERVER["socket"] == ":443" {
ssl.engine = "enable"
ssl.pemfile = "/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/web.pem" # Combined Certificate
ssl.ca-file = "/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/chain.pem" # Root CA
server.name = "www.example.com" # Domain Name OR Virtual Host Name
server.document-root = "/var/www/html/" # Document Root
server.errorlog = "/var/log/lighttpd/example.com_error.log"
accesslog.filename = "/var/log/lighttpd/example.com_access.log"
}
$HTTP["scheme"] == "http" {
$HTTP["host"] == "www.example.com" { # HTTP URL
url.redirect = ("/.*" => "https://www.example.com$0") # Redirection HTTPS URL
}
}
Guarde y cierre el archivo. Luego reinicie el servicio Lighttpd para aplicar los cambios de configuración:
systemctl restart lighttpd
Acceder a la interfaz web de Lighttpd
Lighttpd está instalado y configurado con soporte para PHP y PHP-FPM. Ahora es el momento de probarlo.
Abra su navegador web y escriba la URL https://www.example.com. Será redirigido a la siguiente página:
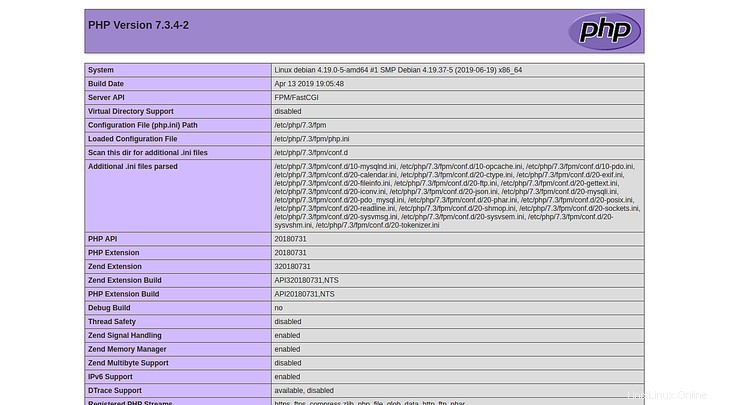
La página anterior indica que PHP funciona bien con FastCGI.
Conclusión
¡Felicidades! ha instalado y configurado con éxito el servidor web Lighttpd con soporte PHP-FPM y FastCGI en Debian 10. Ahora puede alojar su propio servidor web con facilidad. Para obtener más información, visite la página de documentación oficial de Lighttpd en Lighttpd Doc.