oVirt es una solución de virtualización distribuida gratuita y de código abierto que se puede usar para administrar toda su infraestructura. Se basa en Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization y le permite administrar máquinas virtuales, computación, almacenamiento y recursos de red desde la interfaz basada en web. Utiliza el hipervisor KVM y se basa en varios otros proyectos comunitarios, incluidos libvirt, Gluster, PatternFly y Ansible.
En este tutorial, explicaremos cómo instalar oVirt en el servidor CentOS 8.
Requisitos
- Un servidor que ejecuta CentOS 8 con un mínimo de 16 GB de RAM.
- Se configura una contraseña de root en el servidor.
Cómo empezar
Antes de comenzar, deberá configurar el nombre de host FQDN en su sistema. Puedes hacerlo con el siguiente comando:
hostnamectl set-hostname centos.example.com
A continuación, deberá editar el archivo /etc/hosts y vincular la IP de su sistema con el nombre de host.
nano /etc/hosts
Agregue las siguientes líneas:
your-server-ip centos.example.com
Guarde y cierre el archivo cuando haya terminado.
Instalar Repositorio Requerido
A continuación, deberá agregar oVirt y otros repositorios necesarios en su sistema.
Primero, instale el repositorio oVirt con el siguiente comando:
dnf install https://resources.ovirt.org/pub/yum-repo/ovirt-release44.rpm
Una vez instalado, habilite la herramienta de paquete Java, pki-deps y el módulo PostgreSQL con el siguiente comando:
dnf module enable javapackages-tools -y
dnf module enable pki-deps -y
dnf module enable postgresql:12 -y
Una vez que haya terminado, puede continuar con el siguiente paso.
Instalar y configurar oVirt Engine
Primero, actualice el repositorio usando el siguiente comando:
dnf update -y
Una vez que el repositorio esté actualizado, instale oVirt Engine usando el siguiente comando:
dnf install ovirt-engine -y
Una vez completada la instalación, puede configurar oVirt Engine con el siguiente comando:
engine-setup
Se le harán varias preguntas durante la configuración, como se muestra a continuación:
--== PRODUCT OPTIONS ==--
Configure Cinderlib integration (Currently in tech preview) (Yes, No) [No]: Yes
Configure Engine on this host (Yes, No) [Yes]: Yes
Configuring ovirt-provider-ovn also sets the Default cluster.'s default network provider to ovirt-provider-ovn.
Non-Default clusters may be configured with an OVN after installation.
Configure ovirt-provider-ovn (Yes, No) [Yes]: Yes
Configure WebSocket Proxy on this host (Yes, No) [Yes]: Yes
* Please note * : Data Warehouse is required for the engine.
If you choose to not configure it on this host, you have to configure
it on a remote host, and then configure the engine on this host so
that it can access the database of the remote Data Warehouse host.
Configure Data Warehouse on this host (Yes, No) [Yes]: Yes
Configure Grafana on this host (Yes, No) [Yes]: Yes
Configure VM Console Proxy on this host (Yes, No) [Yes]: Yes
--== PACKAGES ==--
[ INFO ] Checking for product updates...
[ INFO ] No product updates found
--== NETWORK CONFIGURATION ==--
Host fully qualified DNS name of this server [centos.example.com]: Yes
[WARNING] Host name Yes has no domain suffix
[ ERROR ] Host name is not valid: Yes did not resolve into an IP address
Host fully qualified DNS name of this server [centos.example.com]:
[WARNING] Failed to resolve centos.example.com using DNS, it can be resolved only locally
Setup can automatically configure the firewall on this system.
Note: automatic configuration of the firewall may overwrite current settings.
Do you want Setup to configure the firewall? (Yes, No) [Yes]: Yes
--== DATABASE CONFIGURATION ==--
Where is the DWH database located? (Local, Remote) [Local]: Local
Setup can configure the local postgresql server automatically for the DWH to run. This may conflict with existing applications.
Would you like Setup to automatically configure postgresql and create DWH database, or prefer to perform that manually? (Automatic, Manual) [Automatic]:
Where is the ovirt cinderlib database located? (Local, Remote) [Local]:
Setup can configure the local postgresql server automatically for the CinderLib to run. This may conflict with existing applications.
Would you like Setup to automatically configure postgresql and create CinderLib database, or prefer to perform that manually? (Automatic, Manual) [Automatic]:
Where is the Engine database located? (Local, Remote) [Local]:
Setup can configure the local postgresql server automatically for the engine to run. This may conflict with existing applications.
Would you like Setup to automatically configure postgresql and create Engine database, or prefer to perform that manually? (Automatic, Manual) [Automatic]:
--== OVIRT ENGINE CONFIGURATION ==--
Engine admin password:
--== SUMMARY ==--
[ INFO ] Restarting httpd
Please use the user '[email protected]' and password specified in order to login
Web access is enabled at:
http://centos.example.com:80/ovirt-engine
https://centos.example.com:443/ovirt-engine
Internal CA 65:FA:CD:BF:DD:2D:F4:99:D6:63:85:80:97:B9:66:B9:C7:29:5A:F3
SSH fingerprint: SHA256:Y46liXyme5Fz/oJA9QaYY1dhK8BKeJiw1kcSjOYL204
[WARNING] Less than 16384MB of memory is available
Web access for grafana is enabled at:
https://centos.example.com/ovirt-engine-grafana/
Please run the following command on the engine machine centos.example.com, for SSO to work:
systemctl restart ovirt-engine
--== END OF SUMMARY ==--
[ INFO ] Stage: Clean up
Log file is located at /var/log/ovirt-engine/setup/ovirt-engine-setup-20200830105920-2u1ydn.log
[ INFO ] Generating answer file '/var/lib/ovirt-engine/setup/answers/20200830110513-setup.conf'
[ INFO ] Stage: Pre-termination
[ INFO ] Stage: Termination
[ INFO ] Execution of setup completed successfully
Después de una instalación exitosa, debe obtener la URL de la consola de administración de oVirt y el panel de Grafana en el resultado anterior.
Configurar SELinux y Firewall
De manera predeterminada, SELinux está habilitado en CentOS 8. Por lo tanto, deberá configurar SELinux para oVirt. Puedes configurarlo con el siguiente comando:
setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1
A continuación, deberá permitir los puertos 80 y 443 a través de firewalld. Puedes hacerlo con el siguiente comando:
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone public --add-port 80/tcp
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone public --add-port 443/tcp
firewall-cmd --reload
Una vez que haya terminado, puede continuar con el siguiente paso.
Acceder a la consola de administración de oVirt
Ahora, abra su navegador web y escriba la URL https://centos.example.com/ovirt-engine/sso/login.html. Debería ver la página de inicio de sesión de oVirt:
Proporcione el nombre de usuario como administrador y la contraseña que configuró durante la instalación, y haga clic en Iniciar sesión En botón. Debería ver la siguiente pantalla:

Ahora, haga clic en Administración Portal . Debería ver el panel de oVirt en la siguiente pantalla:
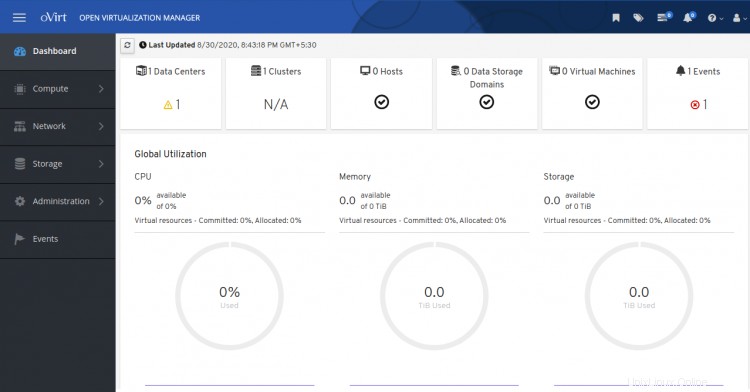
Conclusión
¡Felicidades! ha instalado con éxito oVirt Engine en el servidor CentOS 8. Ahora puede agregar un host de virtualización remoto desde la consola de oVirt y comenzar a crear su primera máquina virtual desde el panel de control de oVirt. Siéntase libre de preguntarme si tiene alguna pregunta.