MariaDB es uno de los sistemas de gestión de bases de datos de código abierto más populares utilizados por pequeñas y grandes empresas. Es una bifurcación del famoso servidor de base de datos MySQL, desarrollado por MariaDB Corporation Ab, dirigido por los desarrolladores originales de MySQL.
MariaDB es totalmente compatible con MySQL para garantizar una capacidad de reemplazo directo. MariaDB se usa a menudo como un servidor de base de datos en la pila LAMP y LEMP.
LEER: Cómo instalar LAMP Stack en CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
LEER: Cómo instalar la pila LEMP en CentOS 8/RHEL 8
En esta publicación, veremos cómo instalar MariaDB en CentOS 8 / RHEL 8.
Instalar MariaDB en CentOS 8/RHEL 8
Puede obtener paquetes de MariaDB para CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 de dos formas.
- Repositorio de Red Hat (v10.3)
- Espejo oficial de MariaDB (v10.4)
Instalar MariaDB desde el repositorio de AppStream
La instalación de MariaDB desde el repositorio de AppStream es sencilla. Pero, el repositorio puede tener una versión un poco antigua del paquete MariaDB.
yum -y install @mariadb
Instalar MariaDB desde el espejo oficial de MariaDB
La fundación MariaDB ofrece paquetes de MariaDB para CentOS 8/RHEL 8. Los paquetes proporcionados por MariaDB siempre están actualizados y son compatibles con la comunidad de MariaDB.
Cent OS 8
cat <<EOF >> /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/centos8-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1 EOF
RHEL 8
cat <<EOF >> /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/rhel8-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1 EOF
Instale el servidor MariaDB usando el siguiente comando.
Necesitamos deshabilitar el repositorio rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms y AppStream temporalmente en RHEL 8 y CentOS 8 respectivamente para permitir que yum descargue paquetes de la réplica de MariaDB.### CentOS 8 ### yum install -y boost-program-options yum --disablerepo=AppStream install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-client ### RHEL 8 ### yum --disablerepo=rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-client
Administrar el servicio MariaDB
En caso de que desee iniciar/detener el servicio MariaDB, puede utilizar los siguientes comandos.
systemctl start mariadb systemctl stop mariadb
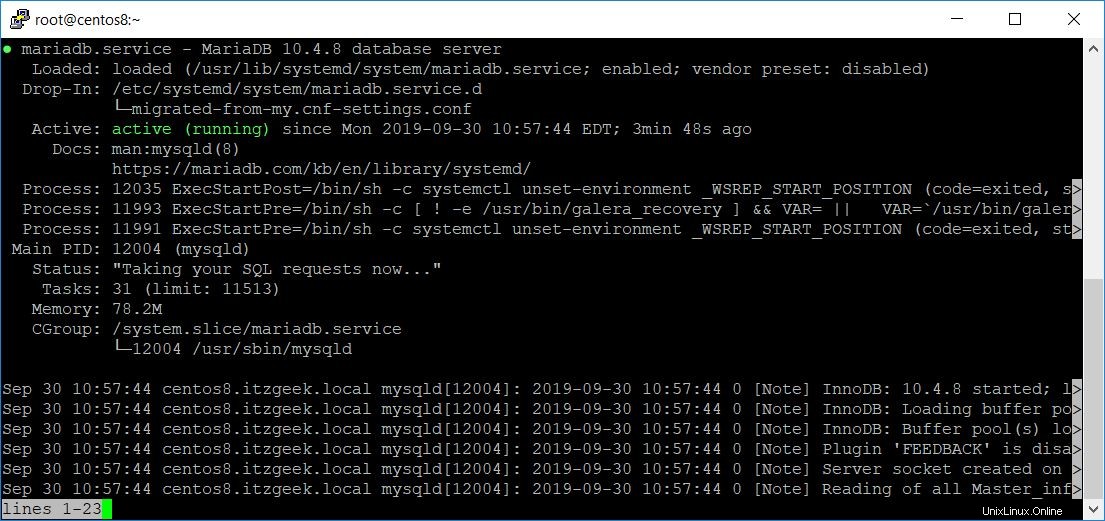
Verifique si MariaDB se está ejecutando o no.
systemctl status mariadb
Instalación segura de MariaDB
Utilice el comando mysql_secure_installation para realizar la configuración inicial del servidor MariaDB. Se recomienda ejecutar este comando en servidores de producción. Elimina el usuario anónimo, la base de datos de prueba y no permite el inicio de sesión raíz remoto.
mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): << Just Press Enter
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody
can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] N << Disable Unix Socket Authendication to Enable Password Authentication
... skipping.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Change the root password? [Y/n] Y << Set MariaDB root password
New password: << Enter root password
Re-enter new password: << Re-Enter root password
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y << Remove Anonymous user
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y << Disallow root login remotely
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y << Remove test database
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y << Reload privilege tables
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Acceder a MariaDB
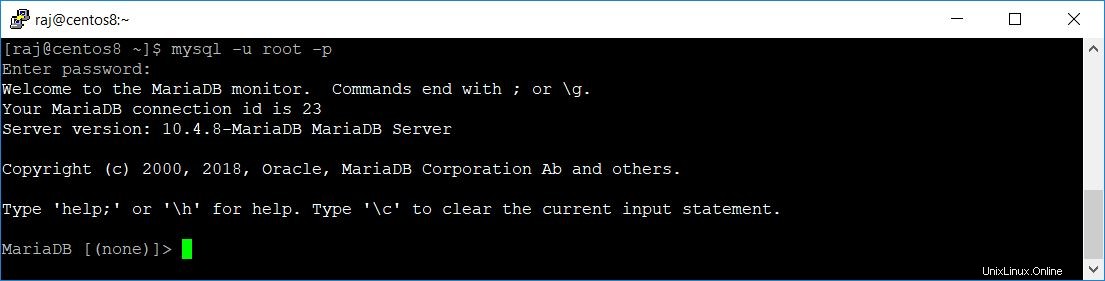
Inicie sesión en el servidor MariaDB con el siguiente comando.
mysql -u root -pSe requiere contraseña
Conclusión
Eso es todo. En esta publicación, aprendió cómo instalar MariaDB en CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 y cómo realizar la configuración inicial. Lea los artículos para principiantes de MariaDB para obtener más información sobre cómo trabajar con MariaDB.