El Network Time Protocol (NTP) se utiliza para sincronizar la hora de un cliente o servidor de computadora con otro servidor. Para instalar ntp en centos 7 usando los siguientes comandos:
[root@thehackertips ~]# yum -y install ntp
Para configurar el servidor ntp, debe abrir el archivo de configuración /etc/ntp.conf .
# Hosts on local network are less restricted.
restrict 172.16.171.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
# add your ntp server here
server 0.az.pool.ntp.org
#broadcast 192.168.1.255 autokey # broadcast server
#broadcastclient # broadcast client
#broadcast 224.0.1.1 autokey # multicast server
#multicastclient 224.0.1.1 # multicast client
#manycastserver 239.255.254.254 # manycast server
#manycastclient 239.255.254.254 autokey # manycast client
Si tiene activado el cortafuegos, puede agregar ntp a la lista de permitidos del cortafuegos y reiniciar el servicio del cortafuegos.
[root@thehackertips ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=ntp --permanent
[root@thehackertips ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
Puede probar el servicio ntp ntpq -p comandos
Para iniciar, detener, reiniciar y ver el estado del servicio ntp, puede ejecutar los comandos de la siguiente manera:
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl status ntpd
ntpd.service - Network Time Service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpd.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2019-10-21 07:01:13 EDT; 1 day 1h ago
Process: 592 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/ntpd -u ntp:ntp $OPTIONS (code=exited, status =0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 603 (ntpd)
CGroup: /system.slice/ntpd.service
ââ603 /usr/sbin/ntpd -u ntp:ntp -g
ââ604 /usr/sbin/ntpd -u ntp:ntp -g
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl stop ntpd
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl start ntpd
[root@thehackertips ~]# systemctl restart ntpd
Configurar servidor SSH
SSH está instalado en Centos 7 de forma predeterminada, sin embargo, es necesario configurarlo por motivos de seguridad. SI no está instalado por algún motivo, puede instalarlo con estos comandos:
[root@thehackertips ~]# yum -y install openssh-server openssh-clients
[root@thehackertips ~]# service sshd start
Para realizar alguna configuración en SSH, debe editar el archivo de configuración:/etc/ssh/sshd_config.
Hay algunas configuraciones principales en SSH que debe seguir:deshabilite el acceso SSH para el usuario root, cambie el puerto predeterminado de ssh y permita el acceso ssh solo para los usuarios requeridos. Para hacerlo, debe abrir el archivo de configuración y agregar esas líneas como se muestra a continuación:
[root@thehackertips ~]# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# Add or configure these lines
Port 1234 # for example 1234
PermitRootLogin no # change Yes to No
AllowUsers user1, user2 # user1 and user2 are the ssh allowed users
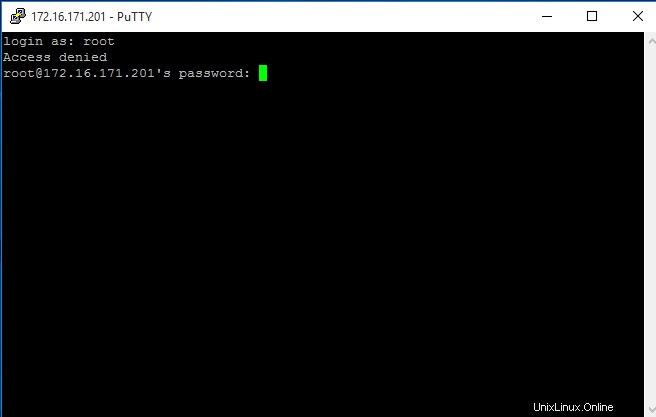
Para conectarse a otro servidor SSH, debe escribir ssh y la dirección IP del host remoto:
[root@thehackertips ~]# ssh 172.16.171.201
The authenticity of host '172.16.171.201 (172.16.171.201)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is ee:3e:9b:e2:9f:3c:b9:cb:33:c6:70:6f:95:c5:9d:ce.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.171.201' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@172.16.171.201's password:
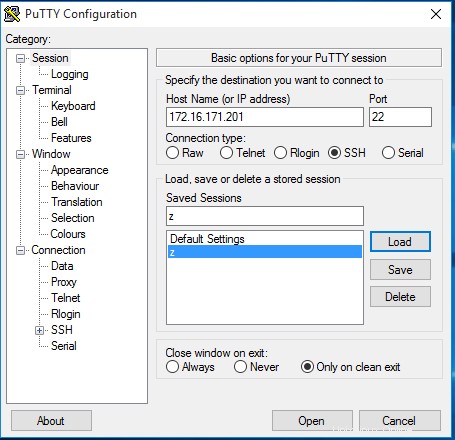
En el cliente de Windows, puede usar Putty para conectarse a Centos 7 con SSH: