A menudo, existe la necesidad de habilitar o deshabilitar los servicios de forma temporal o permanente en nuestro sistema Ubuntu. A veces, es posible que necesitemos que ciertos servicios se inicien automáticamente al arrancar, por ejemplo, ssh o servidores web y, a veces, es posible que necesitemos deshabilitar servicios que ya no necesitamos y que están acaparando la CPU y la RAM.
En este tutorial, echamos un vistazo a cómo podemos habilitar y deshabilitar servicios en Ubuntu. Para hacer esto, primero debemos entender que hay 3 sistemas de inicio principales para Ubuntu
- Systemd
- Advenedizo
- SysV
Cada sistema init tiene una forma diferente de iniciar y detener los servicios. Echaremos un vistazo a cada uno de estos.
Cómo habilitar y deshabilitar servicios en Systemd init
Para iniciar un servicio en systemd ejecute el comando como se muestra:
systemctl start service-namePor ejemplo, para iniciar el servicio web de apache, ejecute
systemctl start apache2Para verificar que el servicio se está ejecutando, ejecute
systemctl status apache2Salida
● apache2.service - LSB: Apache2 web server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/apache2; bad; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
└─apache2-systemd.conf
Active: active (running) since Thu 2018-03-15 17:09:05 UTC; 35s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
├─2499 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
├─2502 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
└─2503 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
Mar 15 17:09:04 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Apache2 web server...
Mar 15 17:09:04 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2475]: * Starting Apache httpd web ser
Mar 15 17:09:05 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2475]: *
Mar 15 17:09:05 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Started LSB: Apache2 web server.Para detener el servicio servicio en ejecución
systemctl stop apache2Para confirmar que el servicio no se está ejecutando, ejecute
systemctl status apache2Salida
● apache2.service - LSB: Apache2 web server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/apache2; bad; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
└─apache2-systemd.conf
Active: inactive (dead) since Thu 2018-03-15 17:19:47 UTC; 12s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 2822 ExecStop=/etc/init.d/apache2 stop (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS
Process: 2687 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/apache2 start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCE
Mar 15 17:10:11 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Apache2 web server...
Mar 15 17:10:11 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2687]: * Starting Apache httpd web ser
Mar 15 17:10:12 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2687]: *
Mar 15 17:10:12 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Started LSB: Apache2 web server.
Mar 15 17:19:46 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Stopping LSB: Apache2 web server...
Mar 15 17:19:46 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2822]: * Stopping Apache httpd web ser
Mar 15 17:19:47 ip-172-31-41-251 apache2[2822]: *
Mar 15 17:19:47 ip-172-31-41-251 systemd[1]: Stopped LSB: Apache2 web server.Para habilitar el servicio apache2 en el arranque, ejecute
systemctl enable apache2Para deshabilitar el servicio apache2 al arrancar, ejecute
systemctl disable apache2Para reiniciar el servicio
systemctl restart apache2Para comprobar si el servicio está actualmente configurado para iniciarse en el próximo arranque
systemctl is-enabled apache2Salida
Executing /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install is-enabled apache2
enabledPara comprobar si el servicio está activo
systemctl is-active apache2Salida
activeCómo eliminar completamente los servicios de Systemd
¿Qué sucede si instaló un paquete y luego decide que ya no lo necesita? ¿Cómo haces para eliminarlo por completo? Siga los comandos a continuación.
Primero, detenga el servicio
systemctl stop service-nameLuego deshabilite el servicio
systemctl disable service-nameEliminar el servicio en systemd
rm /etc/systemd/system/service-namerm /etc/systemd/system/service-name/[related symlinks]Recargar systemd
systemctl daemon-reloadFinalmente corre,
systemctl reset-failedCómo habilitar y deshabilitar servicios en Upstart init
Upstart init system se presentó justo antes de que systemd se usara en Ubuntu 9.10 a Ubuntu 14.10. Más tarde se eliminó pavimentando el camino para systemd init en Ubuntu 15.04 y versiones más nuevas. En este ejemplo, veamos cómo podemos iniciar y detener, habilitar y deshabilitar servicios en Ubuntu 14.04.
Upstart hace uso de archivos de configuración para controlar los servicios. Estos archivos se encuentran en el directorio /etc/init. Estos archivos están formados por secciones de texto sin formato organizadas en estrofas y cada estrofa describe un servicio y cómo funciona.
Para comprobar si un servicio se está ejecutando o no ejecuta el siguiente comando
initctl status service-nameO
service service-name statusO
status service-nameEn este ejemplo, comprobaremos el estado de cups, un servidor de impresión Linux.
initctl status cupsO
service cups statusO
status cupsSalida
cups start/running, process 3029Para detener el servicio ejecute el siguiente comando
initctl stop cupsO
service cups stopO
stop cupsSalida
cups stop/waitingPara habilitar un servicio en Upstart init
En el archivo /etc/init/*.conf, encontrará el "respawn " directiva que inicia un servicio en caso de que se bloquee inesperadamente o si el sistema se reinicia. Normalmente está habilitado de forma predeterminada.
Por ejemplo, en el archivo /etc/init/cups.conf a continuación,
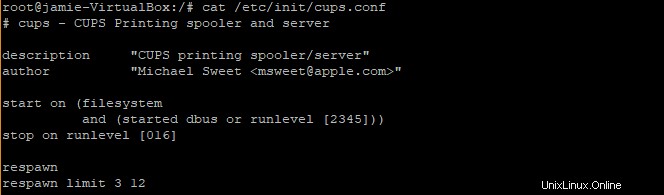
el primer argumento (3) es el número de intentos que intentará reiniciar y el segundo argumento (12) es el intervalo de tiempo entre reintentos. Si no se reinicia automáticamente. se mantendrá en un estado detenido.
Para deshabilitar un servicio en upstart init
ejecuta el siguiente comando
echo manual >> /etc/init/service.override
Esto crea un archivo de anulación que deshabilita un servicio sin alterar la definición del trabajo en absoluto.
Para el servicio de tazas, el comando será
echo manual >> /etc/init/cups.overrideAl reiniciar el sistema, las tazas estarán en un estado detenido. Si desea volver a habilitar el servicio, debe eliminar el archivo /etc/init/cups.override.
Herramienta Sysv-rc-conf
Esta es una consola basada en texto que le brinda una descripción general de los diferentes servicios y niveles de ejecución que están programados para iniciar. Se puede instalar usando el siguiente comando
apt-get install sysv-rc-confPara ejecutar la herramienta, ejecute
sysv-rc-conf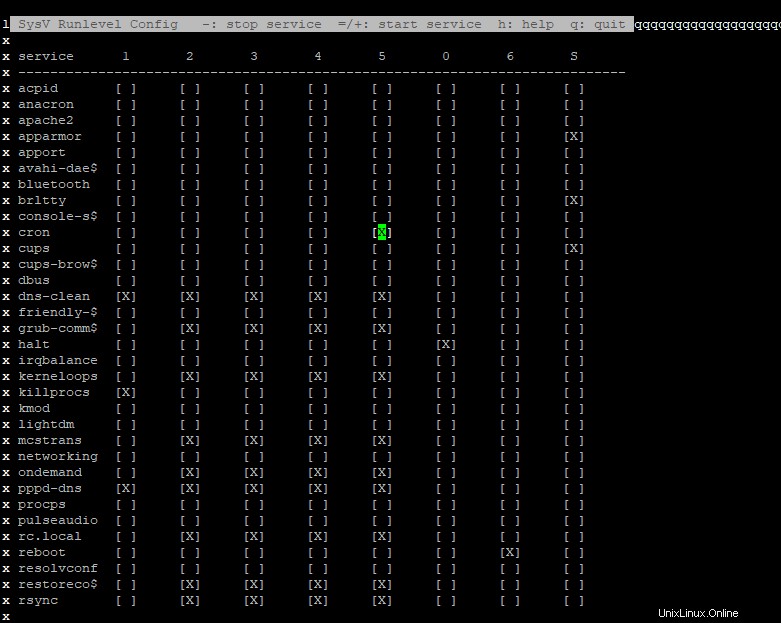
Herramienta de administración de trabajos
Esta es otra característica que le permite controlar servicios y procesos en un entorno GUI. Puede instalar esto ejecutando.
apt-get install jobs-admin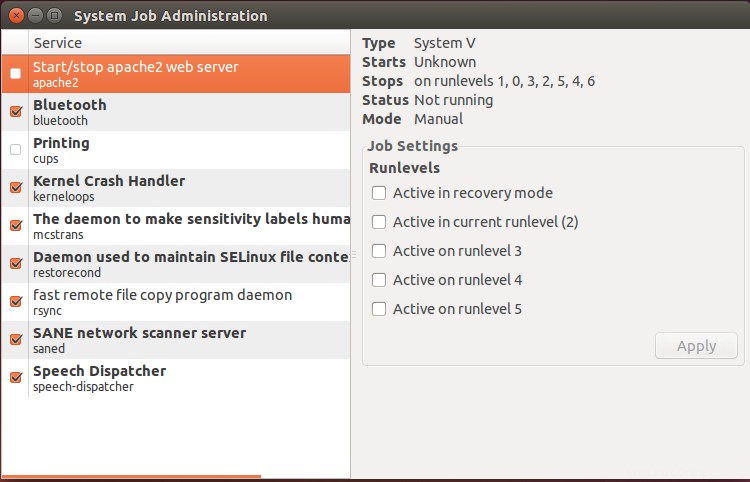
Cómo habilitar y deshabilitar servicios en SysV init
Para habilitar un servicio en SysV init run
update-rc.d enable service-namePor ejemplo, si desea habilitar el servidor web apache, debe ejecutar
update-rc.d enable apache2Para deshabilitar un servicio, ejecute
update-rc.d disable service-namePor ejemplo
update-rc.d disable apache2Casi todos los sistemas Linux se ejecutan en Systemd init de Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL y CentOS. Por lo tanto, descubrirá que utilizará más del comando systemctl para iniciar, detener, habilitar y deshabilitar servicios. Lo invitamos a probar los comandos como se muestra en este artículo. Gracias.
Leer también:
- Comandos Systemctl para administrar el servicio Systemd en Linux