JFrog Artifactory es una aplicación de gestión de repositorios de código abierto que se puede integrar con herramientas de integración y entrega continuas. Es una herramienta multiplataforma que permite a DevOps administrar múltiples repositorios de paquetes. Proporciona alta disponibilidad y replicación en múltiples sitios para automatizar su canalización y permitir lanzamientos más rápidos.
En este tutorial, le mostraremos cómo instalar JFrog Artifactory en Ubuntu 20.04.
Requisitos
- Un servidor con Ubuntu 20.04.
- Un nombre de dominio válido apuntado con su servidor.
- Se ha configurado una contraseña raíz en su servidor.
Instalar JFrog Artifactory
De forma predeterminada, JFrog Artifactory no está disponible en el repositorio predeterminado de Ubuntu 20.04. Por lo tanto, deberá agregar el repositorio JFrog Artifactory a su sistema.
Primero, instale el paquete Gnupg2 con el siguiente comando:
apt-get install gnupg2 -y
A continuación, descargue y agregue la clave GPG con el siguiente comando:
wget -qO - https://api.bintray.com/orgs/jfrog/keys/gpg/public.key | apt-key add -
A continuación, agregue el repositorio JFrog Artifactory con el siguiente comando:
echo "deb https://jfrog.bintray.com/artifactory-debs bionic main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jfrog.list
Una vez que se agrega el repositorio, actualícelo e instale JFrog Artifactory con el siguiente comando:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install jfrog-artifactory-oss -y
Una vez que la instalación se haya completado con éxito, debería obtener el siguiente resultado:
************ SUCCESS ****************
The Installation of Artifactory has completed successfully.
NOTE: It is highly recommended to use Artifactory with an external database (MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MariaDB).
For details about how to configure the database, refer to https://service.jfrog.org/installer/Configuring+the+Database
Start Artifactory with:
> systemctl start artifactory.service
Check Artifactory status with:
> systemctl status artifactory.service
Installation directory was set to /opt/jfrog/artifactory
You can find more information in the log directory /opt/jfrog/artifactory/var/log
System configuration templates can be found under /opt/jfrog/artifactory/var/etc
Copy any configuration you want to modify from the template to /opt/jfrog/artifactory/var/etc/system.yaml
Triggering migration script, this will migrate if needed ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) ...
Processing triggers for systemd (245.4-4ubuntu3) ...
A continuación, inicie el servicio Artifactory y habilítelo para que se inicie al reiniciar el sistema con el siguiente comando:
systemctl start artifactory
systemctl enable artifactory
Luego, verifique el estado del servicio Artifactory usando el siguiente comando:
systemctl status artifactory
Deberías obtener el siguiente resultado:
? artifactory.service - Artifactory service
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/artifactory.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2020-06-07 12:42:39 UTC; 40s ago
Process: 15671 ExecStart=/opt/jfrog/artifactory/app/bin/artifactoryManage.sh start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 17974 (java)
Tasks: 0 (limit: 9522)
Memory: 2.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/artifactory.service
? 17974 /opt/jfrog/artifactory/app/third-party/java/bin/java -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/opt/jfrog/artifactory/app/artifacto>
Jun 07 12:42:38 ubuntu2004 su[18380]: (to artifactory) root on none
Jun 07 12:42:38 ubuntu2004 su[18380]: pam_unix(su:session): session opened for user artifactory by (uid=0)
Jun 07 12:42:38 ubuntu2004 su[18380]: pam_unix(su:session): session closed for user artifactory
Jun 07 12:42:38 ubuntu2004 su[18534]: (to artifactory) root on none
Jun 07 12:42:38 ubuntu2004 su[18534]: pam_unix(su:session): session opened for user artifactory by (uid=0)
Jun 07 12:42:39 ubuntu2004 su[18534]: pam_unix(su:session): session closed for user artifactory
Jun 07 12:42:39 ubuntu2004 su[18655]: (to artifactory) root on none
Jun 07 12:42:39 ubuntu2004 su[18655]: pam_unix(su:session): session opened for user artifactory by (uid=0)
Jun 07 12:42:39 ubuntu2004 su[18655]: pam_unix(su:session): session closed for user artifactory
Jun 07 12:42:39 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Started Artifactory service.
En este punto, Artifactory está instalado y escuchando en el puerto 8082. Ahora puede continuar con el siguiente paso.
Configurar Nginx como proxy inverso
A continuación, deberá configurar Nginx como un proxy inverso para JFrog. Primero, instale el servidor web Nginx con el siguiente comando:
apt-get install nginx -y
Después de instalar Nginx, cree un nuevo archivo de configuración de host virtual de Nginx con el siguiente comando:
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/jfrog.conf
Agregue las siguientes líneas:
upstream jfrog {
server 127.0.0.1:8082 weight=100 max_fails=5 fail_timeout=5;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name jfrog.linuxbuz.com;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://jfrog/;
}
}
Guarde y cierre el archivo, luego active el host virtual Nginx con el siguiente comando:
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/jfrog.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Luego, verifique el Nginx para cualquier error de sintaxis con el siguiente comando:
nginx -t
Debería ver el siguiente resultado:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Finalmente, reinicie el servicio Nginx para implementar los cambios:
systemctl restart nginx
En este punto, Nginx está configurado para servir al sitio JFrog. Ahora puede continuar con el siguiente paso.
JFrog seguro con Let's Encrypt SSL
Se recomienda asegurar JFrog con Let's Encrypt SSL. Primero, agregue el repositorio de Certbot con el siguiente comando:
apt-get install software-properties-common -y
add-apt-repository ppa:ahasenack/certbot-tlssni01-1875471
A continuación, actualice el repositorio e instale el cliente Certbot con el siguiente comando:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
Una vez que el cliente de Certbot esté instalado, ejecute el siguiente comando para descargar e instalar Let's Encrypt SSL para su sitio web:
certbot --nginx -d jfrog.linuxbuz.com
Se le pedirá que proporcione su correo electrónico válido y acepte el término de servicio como se muestra a continuación:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for jfrog.linuxbuz.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/jfrog.conf
A continuación, seleccione si desea redirigir o no el tráfico HTTP a HTTPS:
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
Tipo 2 y pulsa enter para iniciar el proceso. Una vez que se haya instalado el certificado, debería ver el siguiente resultado:
Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/jfrog.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://jfrog.linuxbuz.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=jfrog.linuxbuz.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/jfrog.linuxbuz.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/jfrog.linuxbuz.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2020-09-07. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal. - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le - We were unable to subscribe you the EFF mailing list because your e-mail address appears to be invalid. You can try again later by visiting https://act.eff.org.
Acceder a la interfaz de usuario web de Artifactory
Ahora, abra su navegador web y escriba la URL https://jfrog.linuxbuz.com. Será redirigido a la siguiente página:
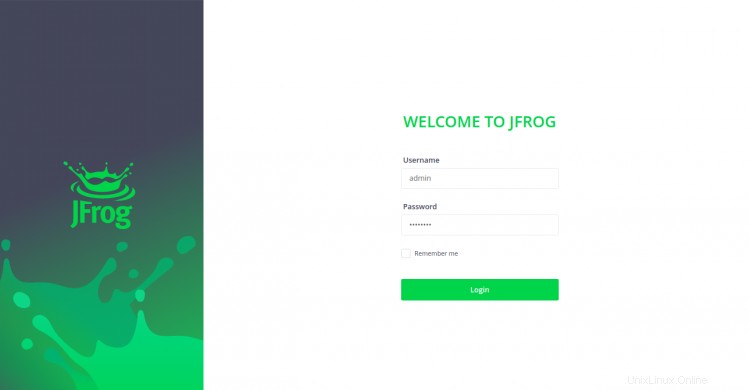
Proporcione el nombre de usuario predeterminado como "administrador" y la contraseña como "contraseña" y haga clic en Iniciar sesión botón. Debería ver la siguiente página:
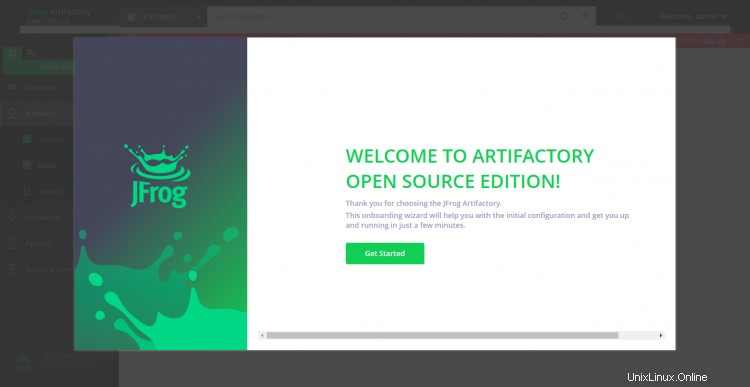
Ahora, haga clic en Obtener Iniciado botón. Debería ver la pantalla de restablecimiento de contraseña:
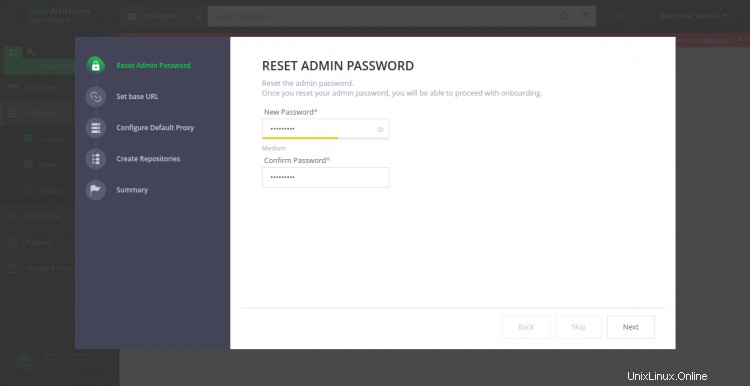
Establezca la nueva contraseña de administrador y haga clic en Siguiente botón. Debería ver la siguiente pantalla:
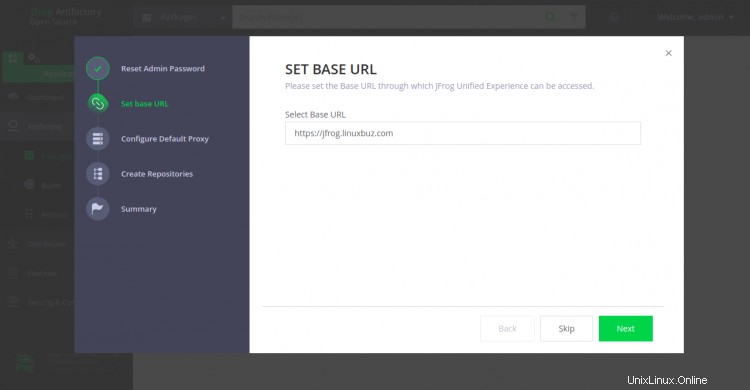
Establezca su URL base y haga clic en Siguiente botón. Debería ver la siguiente pantalla:
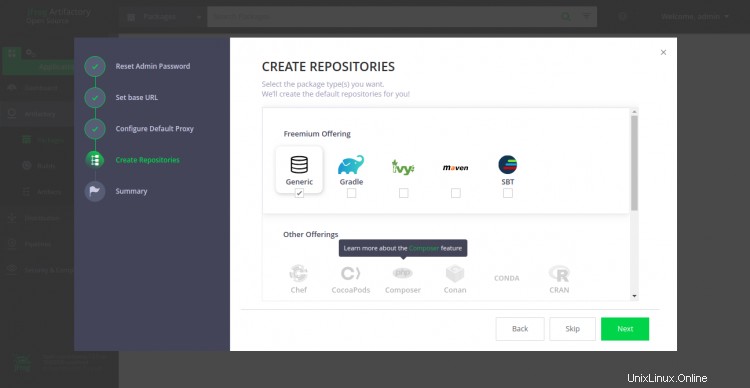
Seleccione el repositorio deseado y haga clic en Siguiente botón. Debería ver la siguiente página:
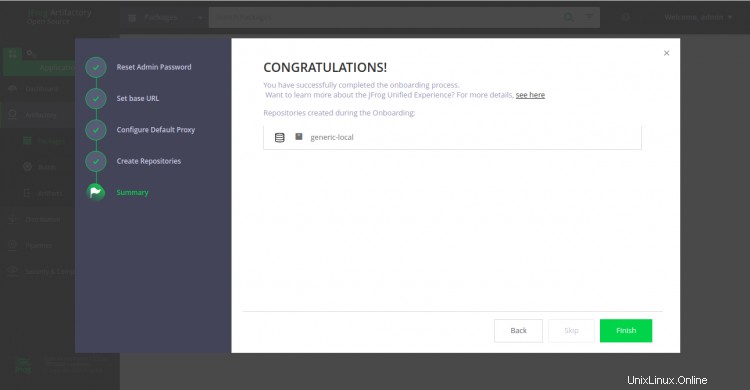
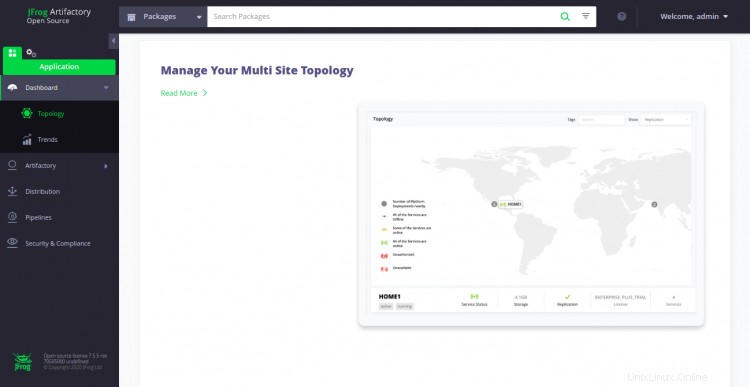
Ahora, haga clic en el botón Finalizar. Debería ver el panel de Artifactory en la siguiente pantalla:
Conclusión
En la guía anterior, aprendimos cómo instalar JFrog Artifactory en Ubuntu 20.04. También aprendimos cómo asegurar JFrog con Let's Encrypt SSL. Espero que ahora pueda instalar fácilmente JFrog en el entorno de producción. Siéntase libre de preguntarme si tiene alguna pregunta.